Thermodynamics is a branch of physical science that treats various phenomena of heat, including the properties of matter, specially the laws of transformation of heat into other forms of energy and vice versa.
Matter – is anything that occupies space and has weight
Properties – characteristic of matter with is quantifiable
2 basic categories of properties of matter
- Extensive – mass dependent
- Intensive – mass independent
Extensive Properties
- mass – Amount of matter in a substance
- volume – space occupied by matter
- weight – force exerted by gravity on a given mass
Mass weight relations
English Metric SI
W lbf kgf W
M slug hyl kgm
g Fb/s^2 m/s^2 m/s^2
a = 32.2ft/s^2 9.8 m/s^2 9.81 m/s^2
Second Law of Newton (Law of Motion)
– state that the acceleration of a particular body is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely to its mass.
Example of Thermodynamics Problems with Solution
Problem # 1:
What is the weight of 66 kgm man at standard condition.
W = mg
m = kgm
g = 9.8
Problem # 2:
What is the weight of an object is 50lb. What is its at standard condition.
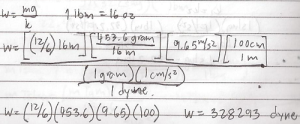
Problem # 3:
What is the mass in grams and the weight in dynes and gram force of 12 oz salt? Local acceleration is 9.65 m/s^2?
Problem # 4:
Five masses in a region where the acceleration due to gravity is 30.5 ft/s^2 are as follows: M1 is 500gm, M2 weighs 800gf, M3 weighs 15 poundals, M4 is 0.10 slug of mass. What is the total mass expressed in a pounds (b) slugs (c) grams.

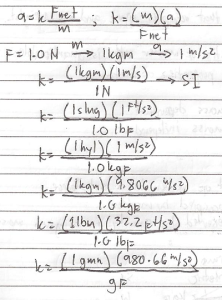


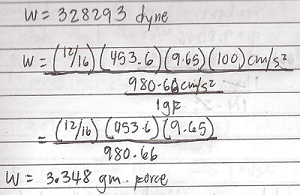


Where did 100/30 m/s^2 came from?
In problem #3 you forgot the 100cm/1m conversion, that resulted to false answers.. Thanks alot..