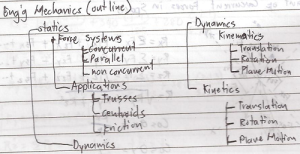
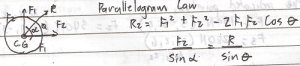Engineering Mechanics is the science which considers the effects of forces on rigid bodies. The subject is divided into two parts.
- Statics – the effects and distribution of force on rigid bodies which are and remain at rest.
- Dynamics – consider the motion of rigid bodies caused by the forces acting upon them.
– is any arrangement where two or more forces act on a body or on a group of related bodies
Resultant of two concurrent coplanar forces
Resultant of two or more Concurrent coplanar
Resultant of Concurrent Forces in Space
Example:
Given the three concurrent forces which through (1, -3, 4) and the indicated points
F1 = 150N (5, -6, 2)
F2 = 340N (4, 0, -3)
F3 = 280N (-1, 2, 6)
Determine the magnitude of resultant force.
Solution: Resolution of Forces