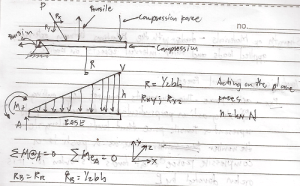
Analysis of External Forces
Pxx – axial force. This components measured the pulling or pushing action perpendicular to the section a pull represents a Tensile force that tends to elongate the member. Where as a push is a compressive force that tends to shorten it. It is often denoted by P .
Pxy Pxz – sheurforces these are compounds of the total resistance to sliding the portion to one side of the exploratory section past the other. The resultant shear force is usually designated by V and its components by Vy and Vz to identify their directions.
Mxx – Torque this components measures the resistance to twisting the number and is commonly given the symbol T .
Mxy Mxz – Bending Moments these component, measures the resistance to bending the member about the y and z axes and are often denoted by My or Mz .
Example:
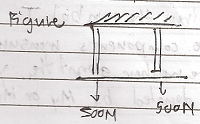
Consider two Bars of Equal length but of different materials suspended from a common support with a maximum axial loads 500N for BAR 1 and 500N for BAR 2, BAR 1 has a cross sectional are of 10mm2 and for BAR 1 has an area of 1000 mm2 which material is stronger.